Gum Disease Treatment in Dedham
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is a condition primarily caused by bacteria found in plaque. The bacteria inflame and infect the gum tissues, and when left untreated, the gums can eventually begin to pull away from the teeth. Untreated periodontal disease can result in bone loss, tooth loss and gum tissue recession.
If your gums are swollen, red or tender, or if your gums bleed easily, you may have periodontal disease. Following an exam at our practice, our team will be able to determine whether you suffer from periodontal disease. The treatment for gum disease is based upon your specific needs. After examination we will be able to recommend a treatment designed for you.

What is a gum disease (periodontal disease)
The term periodontal means “around the tooth.” Periodontal disease (also known as periodontitis and gum disease) is a long-term infection of the gums, bone, and other tissues that surround and support the teeth.
Periodontal disease is most often preceded by gingivitis which is a bacterial infection of the gum tissue. A bacterial infection affects the gums when the toxins contained in plaque begin to irritate and inflame the gum tissues. Once this bacterial infection colonizes in the gum pockets between the teeth, it becomes much more difficult to remove and treat. Periodontal disease is a progressive condition that eventually leads to the destruction of the connective tissue and jawbone. If left untreated, it can cause shifting teeth, loose teeth, and eventually tooth loss.
Periodontal disease should always be promptly treated as it is the leading cause of tooth loss among adults in developed countries.
Signs of Periodontics
In most cases gum disease is painless so it is important that you take good care of your oral health. Regular dental checks are essential.
Signs of gum disease can be subtle. Symptoms may include:
- inflamed or swollen gums
- discolored plaque or tartar on the teeth
- bleeding while brushing or flossing
- halitosis, or bad breath
- pain when eating or chewing
- sensitive teeth
- receding gums, which make the teeth look longer
- extra spaces between the teeth
- pus between the teeth and gums
- a metallic taste in the mouth
- loose or lost teeth
- changes in the way the teeth feel when biting
- changes in the fit of partial dentures
Some people suffering from gum disease experience no symptoms or pain. The best prevention is regular visits with your dental hygienists, this will help keep your oral health in check and catch early stages of gum disease before it progresses.
What can Dr. Anna Vishart do for you
Often times, the signs and symptoms of gum disease may not seem uncommon. However, early diagnosis and treatment can help save your smile and health from life-threatening conditions. Our skilled team at Digital Dental Studio is specialize in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease.
We offer the following periodontal treatments:
Scaling and root planning – This treatment entails deep cleaning between the gum and the tooth to the root. Scaling and root planing is a more invasive form that is preserved for moderate infection.
Regeneration – Depending on the advanced stage of your disease, we may perform a bone graft to stimulate new bone growth, or we may apply a special kind of protein that stimulates tissue growth to repair the areas that have been destroyed by the disease.
Pocket Depth Reduction – also known as flap surgery, it’s a procedure where we fold back the gum tissue and remove the bacteria hiding underneath, as well as the hardened plaque and tartar that has collected. We may also remove any tissue that is too damaged to survive. We then sew the healthy tissue back into place.
Laser gum treatment – Dr. Vishart uses cutting -edge soft tissue lasers to help combat the signs of gum disease. This advanced technology is used in a wide range of gum treatments and offers heightened precision and control. Laser treatments are also preferred by most patients because they are generally faster and less painful than conventional and surgical gum treatments.
Gum Disease Q&A
How did I get gum disease?
Certain factors can increase a patient’s risk of developing periodontal disease, being these the most common:
- Poor oral hygiene: neglecting to brush and floss the teeth daily make the teeth a fertile ground for bacteria that cause gingivitis. If gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis
- Smoking or using chewing tobacco: Bad habits, such as smoking and chewing tobacco, make it hard for damaged gum tissue to repair itself. In time, this can lead to gum disease.
- Hormonal changes: Changes in the hormones that occur during puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can make your gums more sensitive, increasing the chances of gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can advance to gum disease.
- Illnesses: Diseases, such as cancer and HIV, weaken the body’s immune system, which can make the gums more vulnerable to gingivitis-causing bacteria. People with diabetes are at a higher risk because of the body’s reduced ability to use blood sugar.
- Medications: Some drugs can reduce the flow of saliva, which protects the teeth and gums. Some drugs, such as the anticonvulsant Dilantin and the anti-aging Procardia, can cause the gum tissue to grow abnormally. As a result, the gum becomes vulnerable to gum disease.
Can gum disease be fixed?
Gum disease can be fixed. Essentially, it’s all about removing bacteria from your mouth and allowing the gums to heal back to a healthy state. If you want to get rid of gum disease, the first step is to get the right education so that you know how to clean your teeth effectively at home.
Homecare is probably the single most important thing you can do to help cure your gum disease. The hygienist can’t clean your teeth daily so it’s up to you to maintain good oral hygiene, brushing your teeth for two minutes at least twice daily — in the morning and before going to bed — and flossing at least once a day.
The second most important aspect is to get your teeth cleaned professionally. The gum disease must be diagnosed correctly, as there are many different types, and a plan of action must be created.
Does periodontitis hurt?
One of the reasons gum disease is such a problem is that it progresses gradually, often with no pain during the initial stages.
- Gums that bleed when brushing or flossing – No amount of bleeding is normal.
- Red, swollen, or tender gums – Redness can be a sign of irritation or infection. Gums should be a healthy shade of pink or coral.
- Bad breath – Gum disease can be a major contributing factor to persistent bad breath (halitosis).
- Gum recession – Unhealthy gum tissue may begin to recede and pull away from the tooth.
- Loose permanent teeth – As periodontal disease progresses, it can further break down the gum and connective tissues that hold teeth in place.
- Change in bite pattern – As the bone tissue gets destroyed, teeth that were once firmly attached to the jawbone become loose or may shift in position.
What happens if periodontitis is not treated?
Untreated gingivitis will progress into periodontitis, which is a more severe stage of gum disease. The infection and pockets deepen while eating away at your jaw until your teeth become loose and fall out. As gum disease progresses, the gums begin to recede or separate from the teeth and the jaw bone and form periodontal pockets. This can lead to changes in the bite and pain while chewing or biting.
How quickly does periodontitis progress?
Periodontal disease does not happen overnight but over time. There are four periodontal disease stages and they develop at different times. It's important to note each one so you can receive proper treatment.
Periodontitis Stage 1: Initial
Periodontitis Stage 2: Moderate
Periodontitis Stage 3: Severe with potential for tooth loss
Periodontitis Stage 4: Severe with potential for loss of all the teeth.
What do dentists do for gum disease?
In the very early stages - when it is gingivitis - you may just need a professional cleaning from your dental team. They can also give you some great advice and tips on how you can keep your teeth and gums healthy.
If your gum disease is beyond gingivitis, the first step in treating gum disease usually involves scaling and root planing. This treatment may be done over more than one visit, depending on your personal needs.
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the medical term for inflammation of the gums. It is a mild form of gum disease and tends to result in redness, swelling and bleeding of the gum tissue, particularly when you brush or floss your teeth, or bite into something hard like an apple.
Is periodontitis worse than gingivitis?
Without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, or severe gum disease. Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium, which is the gum tissue and bone that keep your teeth in place. As the condition progresses, it can cause teeth to loosen.
How can you tell the difference between periodontitis and gingivitis?
If gingivitis is left untreated, the plaque can accumulate and spread to the gumline. Bacteria in the plaque release toxins, which irritate and inflame the gums.
This triggers a chronic inflammatory response in the body, which damages the gum tissue and bone that keep the teeth in place. The result is periodontitis.
As the gums break down, they pull away from the teeth, creating gum pockets. These gaps can become infected by bacteria in the mouth, causing even more tissue damage.
The tissue damage can also make the gum pockets deeper. If the gaps become too big, the teeth may loosen due to bone loss. Deeper pockets may also mean it’s harder to reach the bacteria when you brush and floss.
How long does gingivitis take to turn into periodontitis?
Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease. At this stage, your gums will start to pull away or "recede" from your teeth.
Can gums grow back?
Unlike skin tissue which has the ability to regenerate, gum tissue cannot. So once your gums star receding it can be problematic if not dealt with.
Can brushing teeth reverse gum disease?
Periodontitis can't be reversed, only slowed down, while gingivitis can be reversed. So keeping an oral health routine like brushing your teeth and flossing at least twice a day will keep your gums healthy and reverse gingivitis.
What are the stages of a gum disease?
Gingivitis
Early Periodontitis
Moderate Periodontitis
Advanced Periodontitis
Is gum recession serious?
When gums recede they pull away from the tooth root structure meaning that the tooth root is often left exposed. Understandably, this can cause tooth sensitivity but can also cause bone tissue loss and eventually, if not treated – the loss of the tooth itself.
Can gum disease affect your brain?
It may sound strange but poor dental health can also affect your brain. The substances released from gums inflamed by infection can damage the brain cells and may lead to memory loss.
At what age do people get periodontal disease?
While periodontitis is more common in older adults it can actually affect younger people without their knowledge, as it starts without obvious trace. However, most people do not begin to show signs until they are in their 30s or 40s.
What is aggressive periodontitis?
This is the worst of the four gum disease stages, causing the most destruction in your gums and bones. The tissues that hold and connect your teeth to the bone will already deteriorate. You're likely to experience extreme pain and also have severe bad breath.
This is also the point where you're at the highest risk of losing your teeth.
Our Services
Restorative
Digital dentistry has taken restorative dentistry to the next level. We manage your oral health problems with less invasive digital precision. Learn more...
Preventive
The only cause of dental decay and periodontal disease and eventually tooth loss due to both, is bacteria that multiply in dental plaque. Learn more...
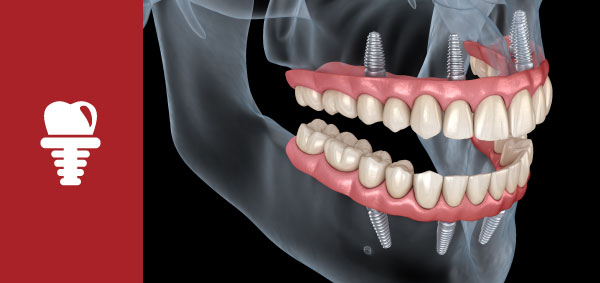
Implants
Introducing our Dental Implants: State-of-the-Art Technology, Minimally Invasive, and Completed in a Single Day! Learn more...
TMJ
TMD or temporomandibular disorder is the loss of synchrony and harmony. Learn more...
Estethics
Dental facial plastics at our Dedham office combine art and science. Learn more...
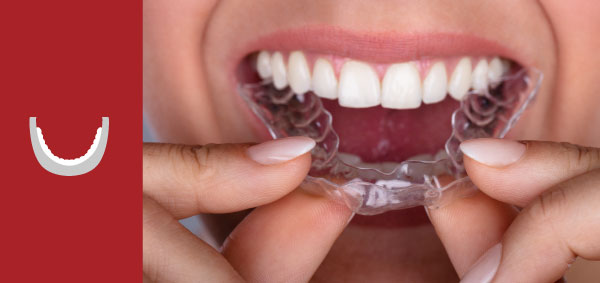
Aligners
Using advanced software technology exact tooth movements can be achieved to ensure anatomically correct teeth alignment with an esthetically pleasing smile. Learn more...